Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) (chemical formula (C8H8)x·(C4H6)y·(C3H3N)z) is a common thermoplastic polymer. Its glass transition temperature is approximately 105 °C (221 °F). ABS is amorphous and therefore has no true melting point.Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a synthetic fluoropolymer of tetrafluoroethylene that has numerous applications. The best known brand name of PTFE-based formulas is polymer by Chemours . Chemours is a spin-off of DuPont Co., which discovered the compound in 1938.
The most important mechanical properties of ABS are impact resistance and toughness. A variety of modifications can be made to improve impact resistance, toughness, and heat resistance. The impact resistance can be amplified by increasing the proportions of polybutadiene in relation to styrene and also acrylonitrile, although this causes changes in other properties. Impact resistance does not fall off rapidly at lower temperatures. Stability under load is excellent with limited loads. Thus, by changing the proportions of its components, ABS can be prepared in different grades. Two major categories could be ABS for extrusion and ABS for injection moulding, then high and medium impact resistance. Generally ABS would have useful characteristics within a temperature range from −20 to 80 °C (−4 to 176 °F).
PTFE is a thermoplastic polymer, which is a white solid at room temperature, with a density of about 2200 kg/m3. According to DuPont, its melting point is 600 K (327 °C; 620 °F). It maintains high strength, toughness and self-lubrication at low temperatures down to 5 K (−268.15 °C; −450.67 °F), and good flexibility at temperatures above 194 K (−79 °C; −110 °F). PTFE gains its properties from the aggregate effect of carbon-fluorine bonds, as do all fluorocarbons. The only chemicals known to affect these carbon-fluorine bonds are highly reactive metals like the alkali metals, and at higher temperatures also such metals as aluminium and magnesium, and fluorinating agents such as xenon difluoride and cobalt(III) fluoride.
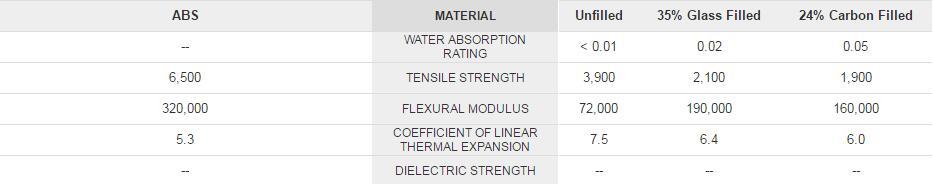
Comparison of Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) and Polymer PTFE/FEP Property Values

Material Applications
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) ![]() ipes and Fittings;Valve bodies, material handling equipment.
ipes and Fittings;Valve bodies, material handling equipment.
polymer PTFE/FEP :Cabling solutions;Non lubricated bearings;O-rings;Seals;Capacitors;Semiconductor manufacturing;High temperature electrical parts;Gaskets;Valve components.
Material Properties
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) :Excellent impact strength;Good fabricating and machining properties;Excellent aesthetic properties;Good chemical resistance;Machines with ease;Low heat conductivity;Corrosion and abrasion resistant;Low co-efficient of friction .
Polymer PTFE/FEP :Excellent dielectric properties;Inertness to most chemicals;High heat and chemical resistance;Very low coeffiecient of friction;Excellent radiation resistance;Zero moisture absorption;Relatively insensitive to power frequency;Machinability.
Post time: Jul-10-2016

