PTFE is a fluorocarbon solid, as it is a high-molecular-weight compound consisting wholly of carbon and fluorine. PTFE is hydrophobic: neither water nor water-containing substances wet PTFE, as fluorocarbons demonstrate mitigated London dispersion forces due to the high electronegativity of fluorine. PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid.
PTFE is very non-reactive, partly because of the strength of carbon–fluorine bonds, and so it is often used in containers and pipework for reactive and corrosive chemicals.

PTFE’s mechanical properties can be enhanced by adding fillers such as glass fibers, carbon, graphite, molybdenum disulphide, and bronze. Generally, filled PTFE’s maintain their excellent chemical and high temperature characteristics, while fillers improve mechanical strength, stability, and wear resistance.
Applications include wear pads, piston rings and rotating platforms in microwave ovens.
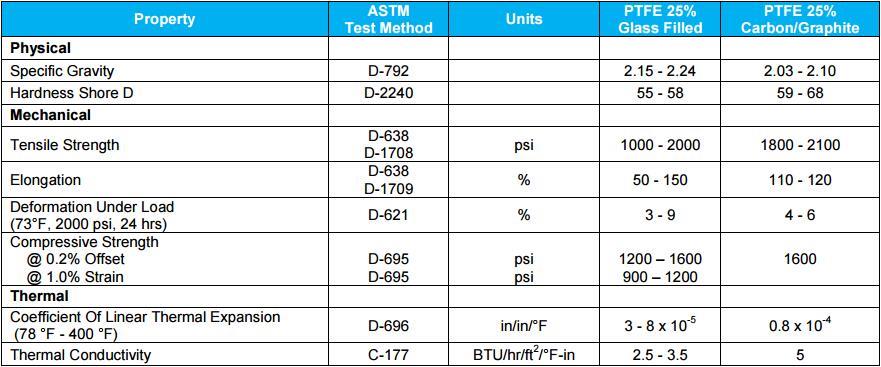
NOTE: The information contained herein are typical values intended for reference and comparison purposes only. They should NOT be used as a basis for design specifications or quality control.
Post time: Feb-14-2020

